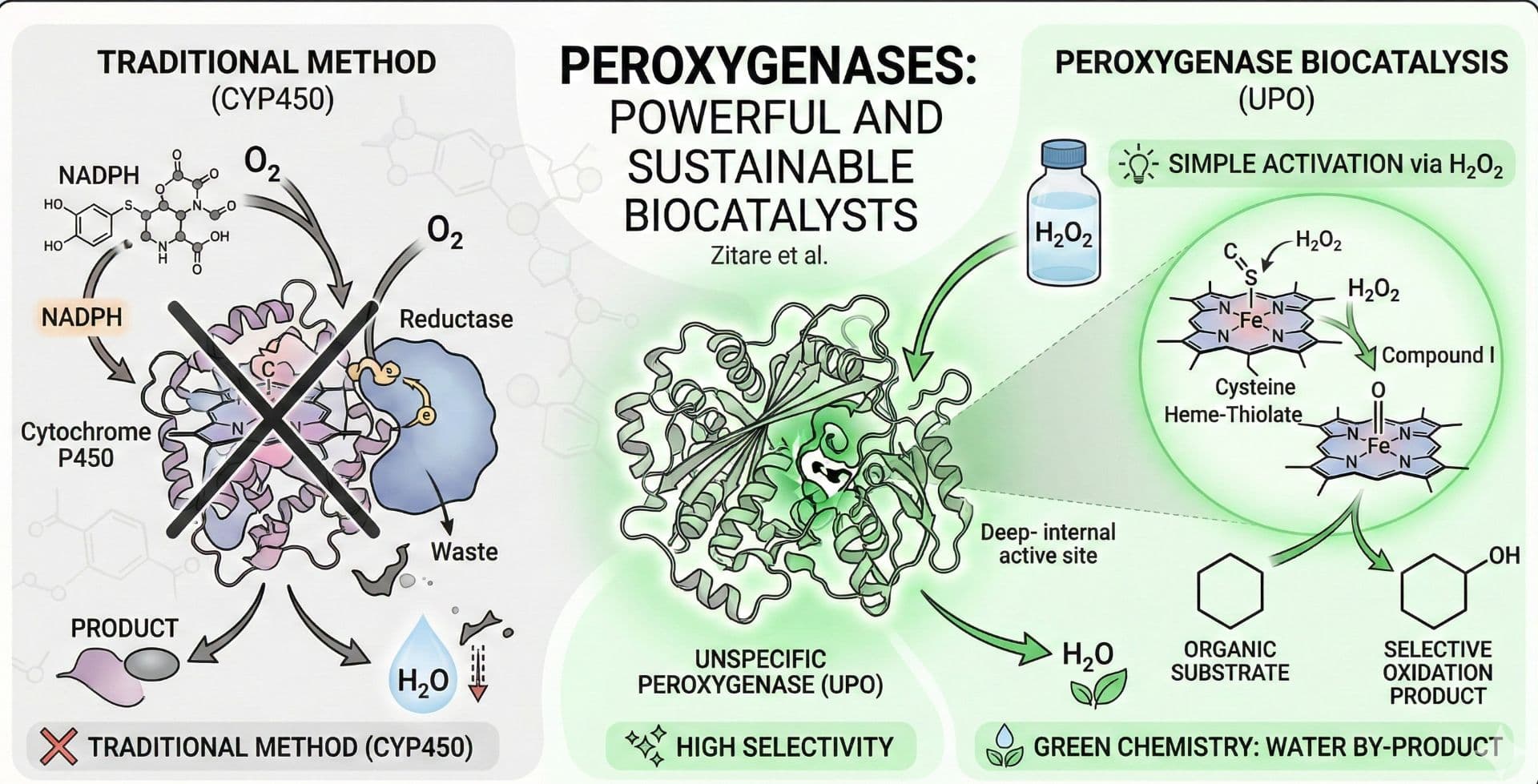
Why Lithium-Ion Batteries Matter
Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular type of rechargeable battery in use today. They power many of the devices we rely on daily, including mobile phones and electric vehicles. These batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged hundreds of times. They are also more environmentally friendly than other types of batteries, as they do not contain toxic heavy metals like lead or cadmium.
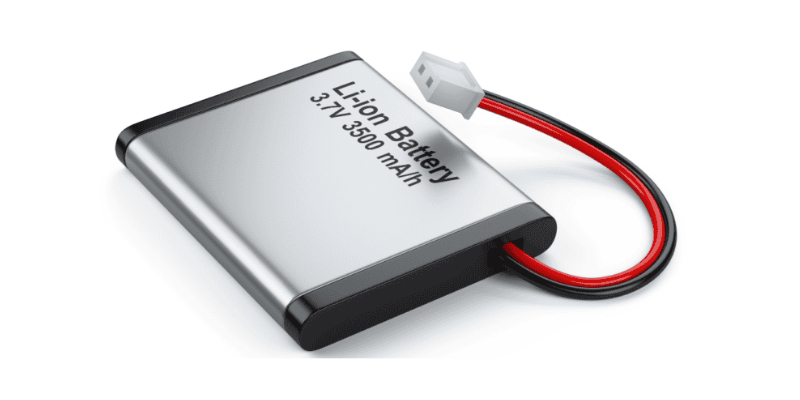

A lithium-ion battery consists of one or more lithium-ion cells and a protective circuit board. They are referred to as batteries once the cells are installed in a device along with the protective circuit board.
What are the components of a lithium-ion cell?
Electrodes: The parts of a cell that are charged positively and negatively. They are attached to the current collectors.
Anode: The electrode that carries a negative charge.
Cathode: The electrode that carries a positive charge.
Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that conducts electricity within the cell.
Current Collectors: Conductive foils located at each electrode of the battery. They connect to the cell terminals, which transmit electric current between the battery, the device it powers, and the energy source charging the battery.
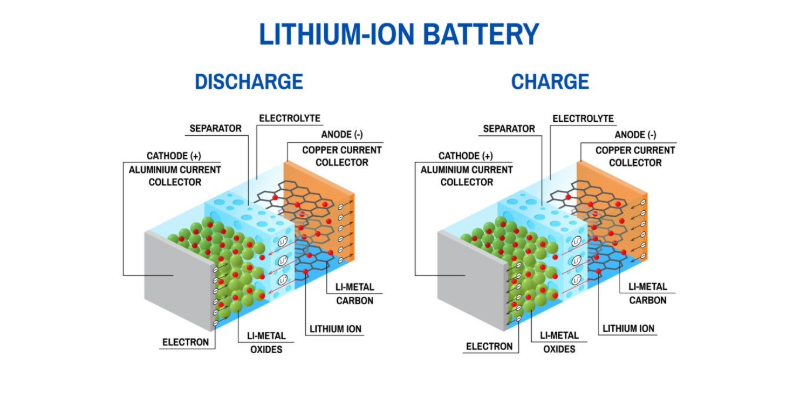
How Does a Lithium-Ion Cell Work?
In a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions (Li+) move internally between the cathode and the anode. Electrons flow in the opposite direction through the external circuit. This movement of ions and electrons is what generates the electrical current to power the device.
During the discharge process, the anode releases lithium ions to the cathode, which generates a flow of electrons that powers the connected device.
When the battery charges, the reverse occurs: lithium ions are released by the cathode and absorbed by the anode.
Separator: A porous polymer film that separates the anode and cathode while allowing the exchange of lithium ions between them.
Discover the essential components of a lithium-ion battery cell, which play a crucial role in powering our modern devices. Understanding these elements can help you appreciate the technology behind our everyday electronics