The Internet: Introduction
The Internet has transformed the world, connecting people, information, and resources in unprecedented ways, even beyond physical boundaries. What began as a small research project has now grown into a global system that supports billions of devices and enables nearly every aspect of modern life. In this article, we will explore the major discoveries and milestones that contributed to the development of the Internet.
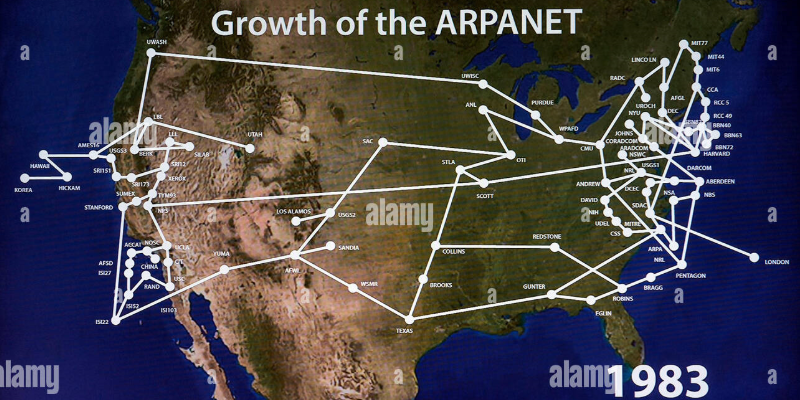
The Birth of the Internet: ARPANET (1969)
The story of the Internet begins with ARPANET, a groundbreaking project funded by the U.S. Department of Defense in the late 1960s. Led by researchers like Paul Baran and Donald Davies, ARPANET introduced packet-switching technology, which breaks data into smaller packets for efficient transmission. This method allows information to travel along multiple paths, ensuring reliable delivery. ARPANET promoted knowledge sharing over long distances by linking computers at various research institutions. This innovation laid the essential groundwork for the Internet, forever changing how we connect and communicate globally.

The Development of TCP/IP (1970s-1980s)
In the 1970s, visionary computer scientists Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn introduced TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), a groundbreaking set of communication protocols that transformed how different types of computers and networks interact. By enabling a decentralized network, TCP/IP ensured that no single computer or institution could dominate the data flow. This innovative open system was essential for the internet's remarkable scalability, allowing it to evolve into the vast interconnected network integral to our lives today.
In 1983, ARPANET adopted TCP/IP as its standard protocol, marking the birth of the modern internet. This development signified the start of a truly global network that would eventually span the entire planet.

The World Wide Web: Revolutionizing Access to Information (1989-1990s)
In 1989, British computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee, working at CERN, introduced the World Wide Web (WWW), a system that used hypertext to link and access documents online. This groundbreaking innovation revolutionized how we create, share, and access information through browsers, servers, and websites.
By 1991, the launch of the first website sparked a digital revolution. Graphical web browsers like Mosaic, which later became Netscape, made the web more accessible and user-friendly. This transformation allowed people from all walks of life to explore the internet, leading to its rapid expansion beyond academic and research communities.

The Rise of Search Engines and the Information Explosion (1990s-2000s)
As the internet grew in the 1990s, more and more information became available online. With billions of websites to choose from, it became harder to find specific content. This problem led to the creation of search engines like AltaVista, Yahoo!, and later, Google.
Google was founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin. It changed how we search for information online using advanced search algorithms. Google ranks webpages using a system called PageRank, which counts the number of links to a webpage. This method helps Google provide more accurate and relevant search results. As a result, the internet became a large, searchable library, making it easy for anyone to find information on almost any topic. An example of a social-media Apps

Social Media and the Web 2.0 Revolution (2000s-Present)
The 2000s marked the rise of Web 2.0, a term used to describe the transition from static websites to more dynamic and interactive platforms. Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn emerged, enabling users to create content, share experiences, and connect with people around the world. These platforms harnessed the power of the internet to foster virtual communities, facilitate communication, and encourage collaboration.
The evolution of Web 2.0 also led to the rise of user-generated content, the creation of blogs, and the sharing of video and multimedia content. The internet transformed from a space solely for accessing information into a platform where individuals could express themselves, build communities, and share their lives.

The Emergence of the Mobile Internet (2000s to Present)
A transformative shift in internet technology occurred with the mobile revolution. The launch of smartphones like the iPhone in 2007 and the expansion of mobile networks put the Internet in the hands of billions worldwide. Mobile apps and responsive websites enhanced accessibility and convenience, enabling connections that once seemed impossible. This change has profoundly altered how we communicate and engage with the world.
More people now access the Internet via mobile devices than through desktop computers. The mobile Internet is evolving thanks to 5G networks, which offer faster speeds, lower latency, and enhanced connectivity.

Cloud Computing and the Future of the Internet (2000s-Present).
In recent years, cloud computing has emerged as one of the most significant advancements in Internet technology. Cloud services enable users to store data, run applications, and access resources over the internet rather than depending on local hardware. Leading companies such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure have pioneered the development of scalable, flexible, and cost-effective cloud infrastructure.

The Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Devices (2010s-Present)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the expanding network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects that are connected to the internet. By utilizing sensors and data analytics, these devices can communicate with one another and share data in real-time. The IoT is revolutionizing various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, and home automation
Smart homes, wearables such as smartwatches, and connected vehicles are a few examples of how the internet is expanding beyond traditional devices like computers and smartphones. The potential of the Internet of Things (IoT) is vast, and it is expected to continue revolutionising sectors such as energy, transportation, and healthcare.
Conclusion: The Internet’s Endless Potential
The internet has undergone significant changes since its inception as a research project in the 1960s. It connects people around the world, making communication, shopping, learning, and entertainment easier than ever. In the future, the internet will continue to evolve. New technologies like 5G, blockchain, and artificial intelligence will help shape the next stage of this digital change.