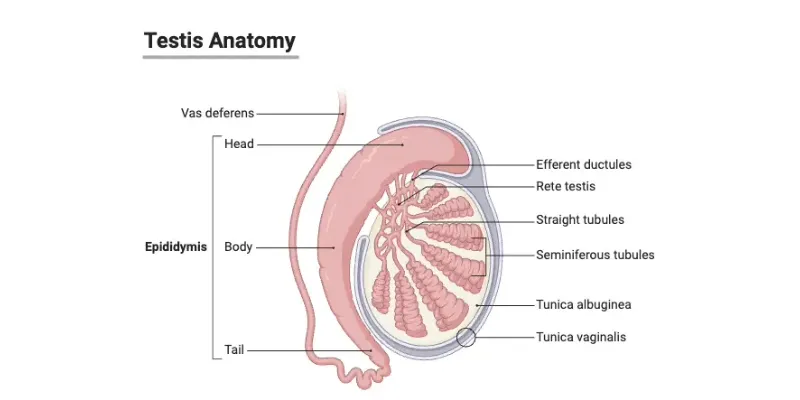
Introduction:
From innovative methods for cancer treatment to understanding the complexities of the human gut biome, these discoveries not only enhance our comprehension of the world but also lay the foundation for future groundbreaking advancements.
Israeli scientists
Israeli scientists from Tel Aviv University and Sheba Medical Center have made a breakthrough in understanding why heart attack survivors have a higher risk of developing cancer.
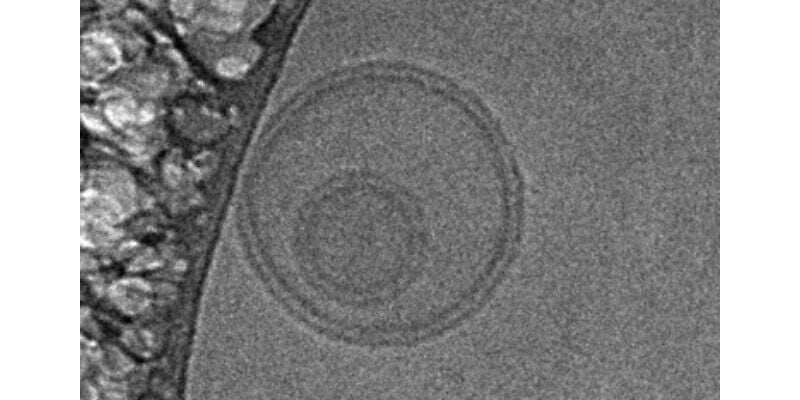
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs)
They found that tiny bubbles released from the recovering heart called small extracellular vesicles (sEVs). They enter the bloodstream and end up “feeding” cancer tumors in other parts of the body.
Caller and his fellow researchers found that a drug commonly used to treat heart disease may be able to reduce or stop the sEVs’ ability to promote cancer.
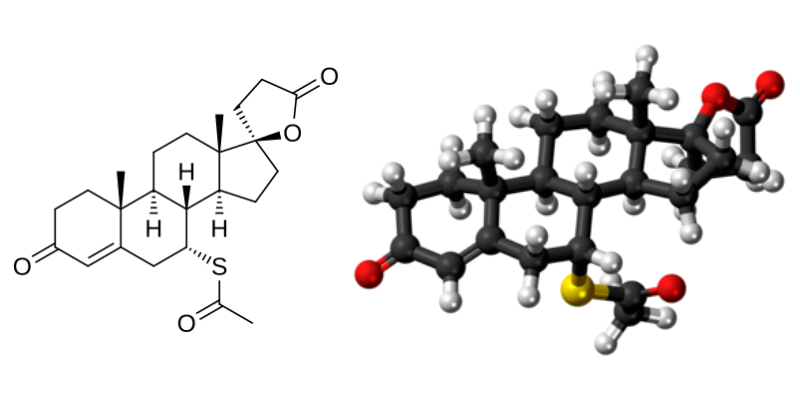
sEVs using drugs such as spironolactone,
By blocking these sEVs using drugs such as spironolactone, The researchers slowed tumor growth by up to 30 percent in animal tests.
The discovery could lead to better treatments for heart attack patients, reducing their cancer risk.
Researchers and clinicians have long observed that people with heart disease also have a greater risk of developing cancer.
Conclusion:
The discovery could lead to better treatments for heart attack patients reducing their cancer risk.